It has a uniform cross section, a complete shape and a highly complete internal structure.It is a non-metallic material with many special properties. Dispersing calcium sulfate Fiber in the epoxy glue A and B components can replace part of the filler. It can improve the strength and adhesive properties of the epoxy glue, and can increase the thixotropic properties of the epoxy glue.
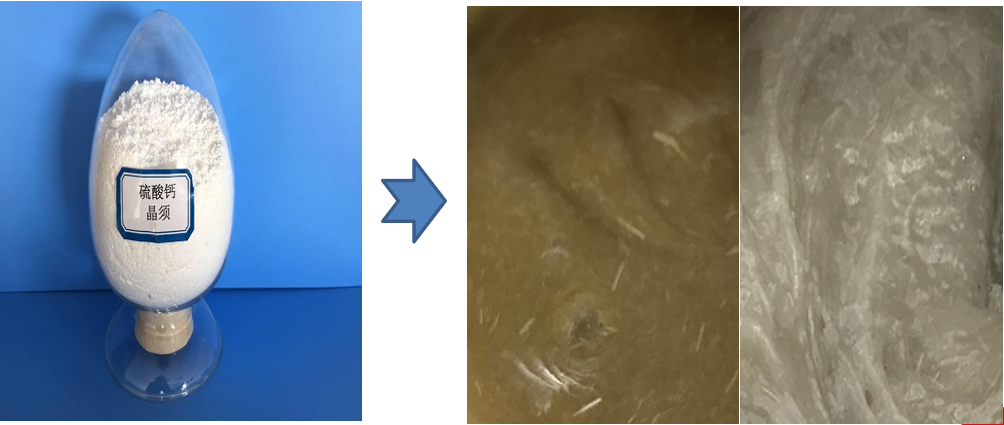
| Chemical Composition | Appearance | Particle Shape | Purity (%) | Length (µm) | Diameter (µm) | L/D Ratio | Whiteness (%) | Gravity (g/cm³) | Loose Density (g/cm³) | Heat Resistant (℃) | Melting Point (℃) | pH Value | Mohs Hardness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaSO4 | White Powder | Rod-like Shape Fiber | ≥95 | 10–100µm (90%) | 1–10µm (90%) | 5–50 (90%) | > 90 | 2.69 | 0.3–0.5 | 1000 | 1450 | 6.5–7.5 | 3 |
Package:
25 KG/Bag (Inner Plastic Bag plus Kraft Paper Bag Outside)
36 bags, 900 kg totally with wrapping onto one composite pallet under ISPM-15 regulation.
Incorporating calcium sulfate fibers, specifically in the form of calcium sulfate whiskers (CSWs), into structural adhesives offers several notable advantages:

Copyright © 2025 Anourav Innovative Materials Pvt Ltd, All rights reserved. Developed & designed by Buzzing Brands